data-mining.md 2.4 KB
EliasDB Data Mining Example
This example demonstrates a more complex application which uses the cluster feature of EliasDB and GraphQL for data queries.
The idea of the application is to provide a platform for data mining with 3 components for presentation, collection and storage of data. The data which is being collected are request response times of the domain devt.de.
The tutorial assumes you have downloaded EliasDB, extracted and build it.
It also assumes that you have a running docker environment with the docker and docker-compose commands being available. This tutorial will only work in unix-like environments.
For this tutorial please execute build.sh in the subdirectory: examples/data-mining and run docker-compose up in the same directory.
After running build.sh you should see the following docker images in the local docker registry:
> docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
data-mining/collector latest 3a159822c9e6 6 minutes ago 174MB
data-mining/frontend latest c412dbd46dce 16 hours ago 22.7MB
data-mining/eliasdb3 latest c079c1ad876e 17 hours ago 20.9MB
data-mining/eliasdb2 latest b53ec5dfdcfb 17 hours ago 20.9MB
data-mining/eliasdb1 latest 83fddb8783df 17 hours ago 20.9MB
After running docker-compose up you should see 5 containers starting with the collector container continuously gathering ping results and storing it into the running EliasDB cluster.
You can query the state of the database by pointing a browser at:
http://localhost:4040/db/term.html
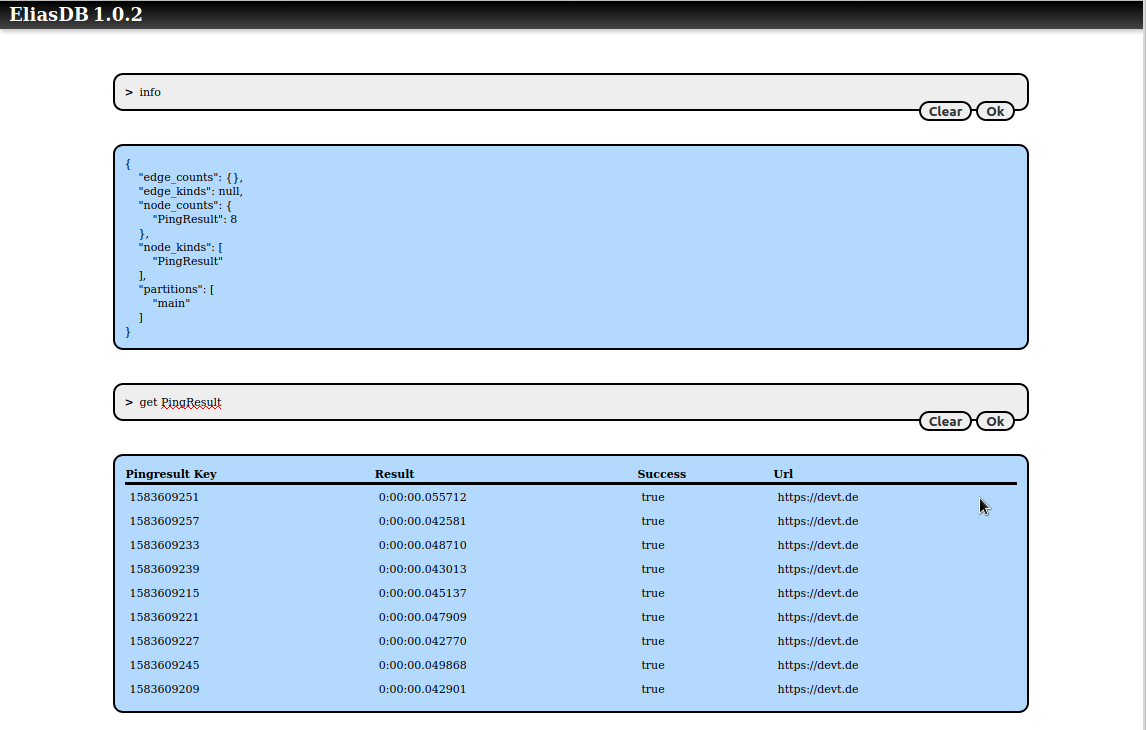
You can query for PingResult nodes:
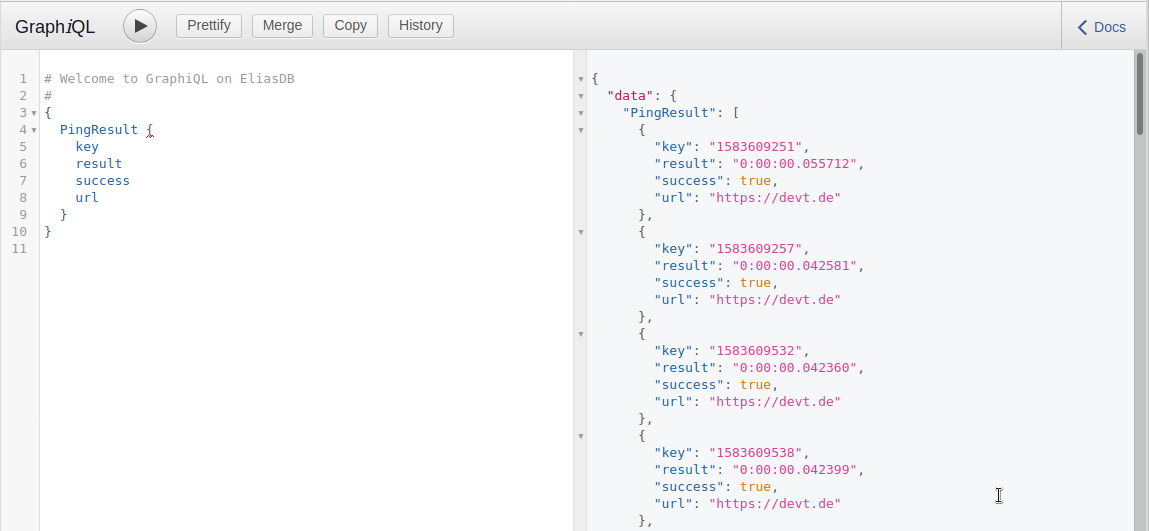
You can also use a GraphiQL interface by pointing a browser at:
http://localhost:4040/graphiql/
You can also here query for PingResult nodes:
You can log into a running EliasDB container and query its disk usage:
> docker exec -it eliasdb1 sh
/data # du -h
2.2M ./db
48.0K ./web/db
56.0K ./web
12.0K ./ssl
2.3M .
/data # df -h
Filesystem Size Used Available Use% Mounted on
overlay 240.1G 43.3G 184.5G 19% /
...
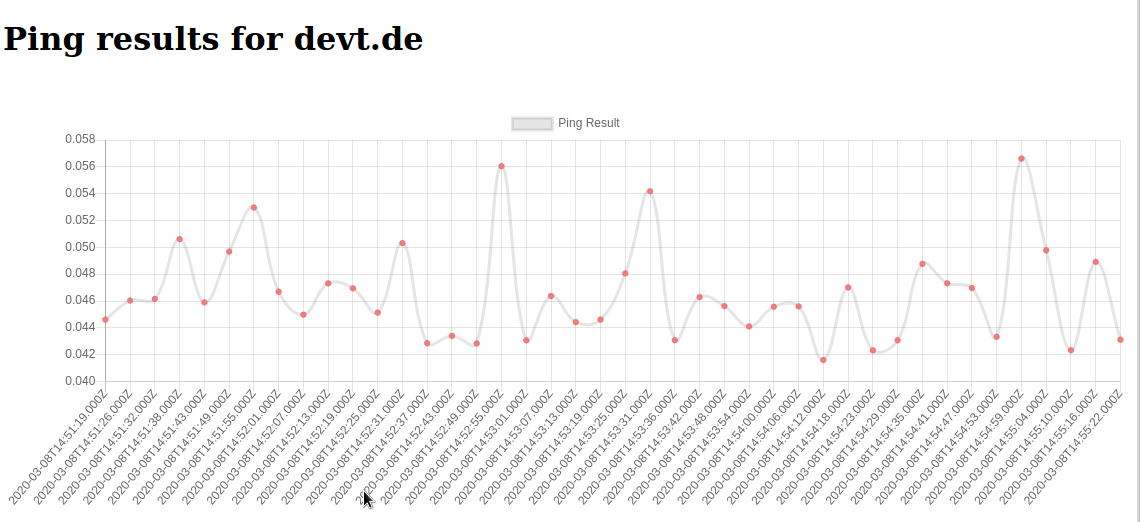
Finally you can see a graph of the collected data by navigating to:
http://localhost:4040/